Etymology
History
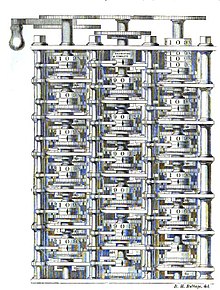
Pre-20th century
First computer
Analog computers
Digital computers
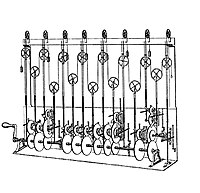
Electromechanical
Vacuum tubes and digital electronic circuits
Modern computers
Concept of modern computer
Stored programs
Transistors
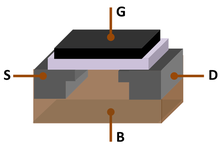
Integrated circuits
Mobile computers
Types
Computers can be classified in some different ways, including:
By architecture
- Analog computer
- Digital computer
- Hybrid computer
- Harvard architecture
- Von Neumann architecture
- Complex instruction set computer
- Reduced instruction set computer
By size, form-faform factorurpose
- Supercomputer
- Mainframe computer
- Minicomputer (a term no longer used)
- Server
- Personal computer
- Mobile computers:
- Wearable computer
- Single-board computer
- Plug computer
- Stick PC
- Programmable logic controller
- Computer-on-module
- System on module
- System in a package
- System-on-chip (Also known as an Application Processor or AP if it lacks circuitry such as radio circuitry)
- Microcontroller
Hardware
History of computing hardware
Other hardware topics
Input devices
- Computer keyboard
- Digital camera
- Digital video
- Graphics tablet
- Image scanner
- Joystick
- Microphone
- Mouse
- Overlay keyboard
- Real-time clock
- Trackball
- Touchscreen
- Light pen
Output devices
Control unit
- Read the code for the next instruction from the cell indicated by the program counter.
- Decode the numerical code for the instruction into a set of commands or signals for each of the other systems.
- Increment the program counter so it points to the next instruction.
- Read whatever data the instruction requires from cells in memory (or perhaps from an input device). The location of this required data is typically stored within the instruction code.
- Provide the necessary data to an ALU or register.
- If the instruction requires an ALU or specialized hardware to complete, instruct the hardware to perform the requested operation.
- Write the result from the ALU back to a memory location or to a register or perhaps an output device.
- Jump back to step (1).
A central processing unit (CPU)
Arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
Memory
Computer main memory comes in two principal varieties:
Input/output (I/O)
Multitasking
Multiprocessing
Software
Languages
Programs
Stored program architecture
This section applies to the most common RAM machine-based computers.
Machine code
Programming language
Low-level languages
High-level languages
Program design
Bugs
Networking and the Internet
Unconventional computers
Future
Computer architecture paradigms
There are many types of computer architectures:
- Quantum computer vs. Chemical computer
- Scalar processor vs. Vector processor
- Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) computers
- Register machine vs. Stack machine
- Harvard architecture vs. von Neumann architecture
- Cellular architecture


















Comments
Post a Comment